Table of Contents
AI in Hospitals– Imagine walking into a hospital where the overwhelming stress on healthcare providers is a thing of the past, and every decision is backed by intelligent, real-time insights. Sounds like a dream? With artificial intelligence in hospitals, the dream of that happening is now a real possibility. The use of AI in hospitals is not only improving patient care but also alleviating likely burnout and increasing efficiencies for overworked medical personnel.
Artificial intelligence (AI) tools automate administrative work, perform sophisticated analytic work, and aid decision-making, enabling clinicians to devote more attention to patient care and less attention to paperwork. A study in the Journal of Medical Internet Research reported a 30% decrease in the administrative burden in hospitals utilizing an AI-based system that resulted in increased job satisfaction and fewer levels of stress among workers.
Using AI in hospitals can not only reduce pressure on healthcare providers but also streamline operations, enhance the quality of care, and decrease errors. As we explore AI’s potential, it’s clear that the technology’s role in healthcare is transformative—empowering professionals, enhancing efficiency, and ultimately improving patient experiences.
Understanding Burnout in Healthcare: The Silent Crisis Impacting Providers
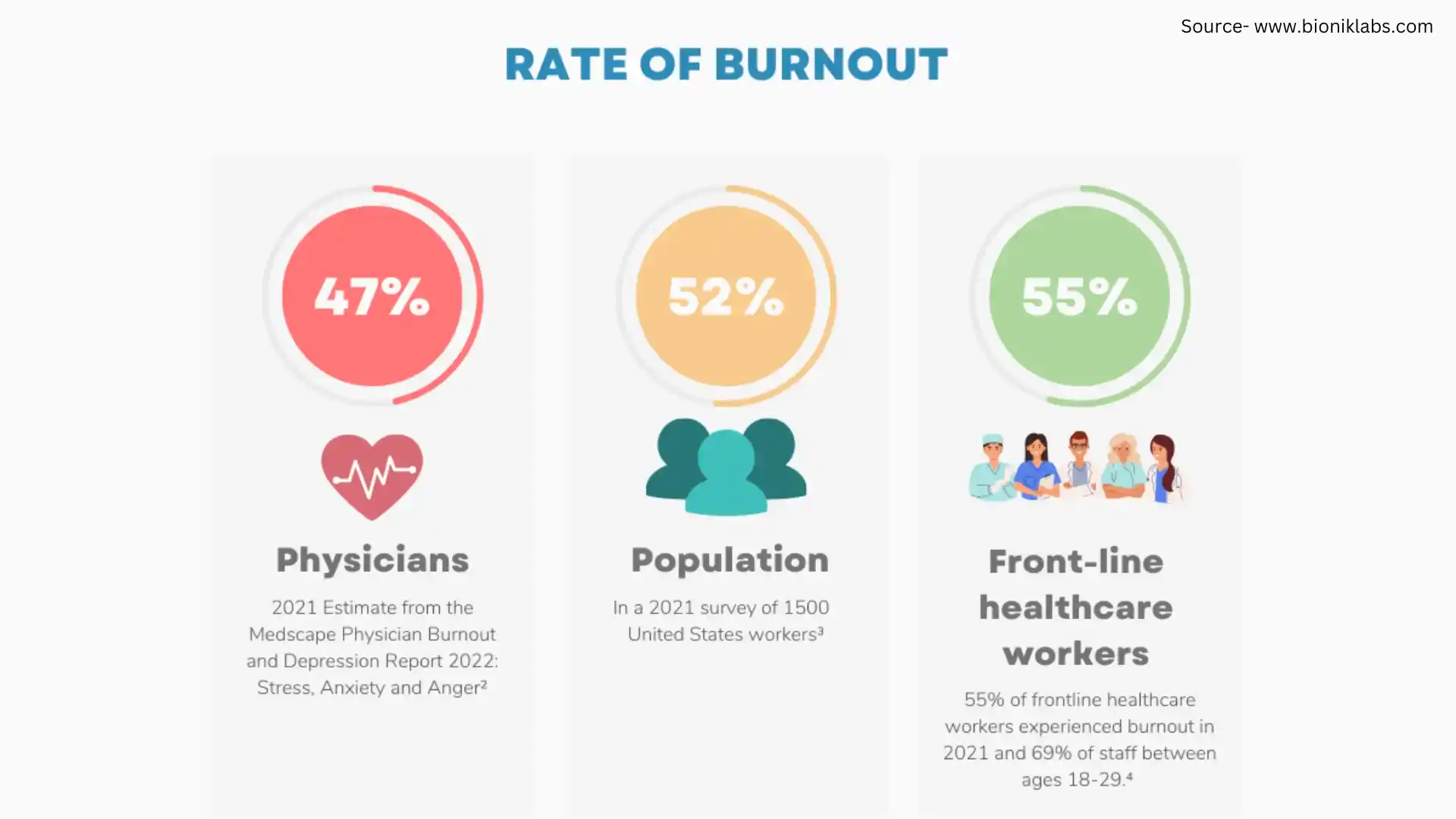
Burnout in the medical field is not just fancy talk but a health crisis on the rise that jeopardizes the well-being of medical personnel and patient care. Defined as a condition resulting from prolonged stress, emotional, and physical fatigue, burnout has great relevance for many health professionals, ranging from nurses all the way to physicians. Indeed, a study by the American Medical Association shows that over 50 of doctors suffer from burnout and similar high rates can also be observed among nurses and other medical personnel.
Stressors in the form of high workload, overtime, emotional depletion, and a poor sense of work process control. Furthermore, clinicians are facing the rising demands for documentation, administration, and the complicated patient care setting. Each of these results in a feeling of powerlessness and frustration, subsequently leading to a drop in work satisfaction and thereby decreases in patients’ quality of care.
According to the NIH National Institutes of Health (University of Maryland, Baltimore), burnout is associated with an increase in medical errors and a decrease in patient satisfaction, with 28% of cases hurting patient care. In addition, burnout leads to high turnover, rendering hospitals understaffed and compromising operational efficiency. This cycle of overwork and poor quality of care is not only detrimental to healthcare providers but also damaging to the whole of the healthcare system.
But there’s hope. While searching for solutions, it is evident that technology, and more specifically, AI in hospitals, opens significant opportunities to both mitigate burnout and optimize the healthcare work environment for both providers and their patients.
How AI in Hospitals Can Help: Alleviating Burnout and Enhancing Efficiency
AI is not just a futuristic concept—it’s already transforming healthcare in ways that directly address the challenges contributing to burnout. Through automation of routine tasks, workflow optimization, and actionable intelligence, AI is facilitating a decrease in the cognitive and administrative burden that leads to fatigue. Here’s how AI in hospitals can help:
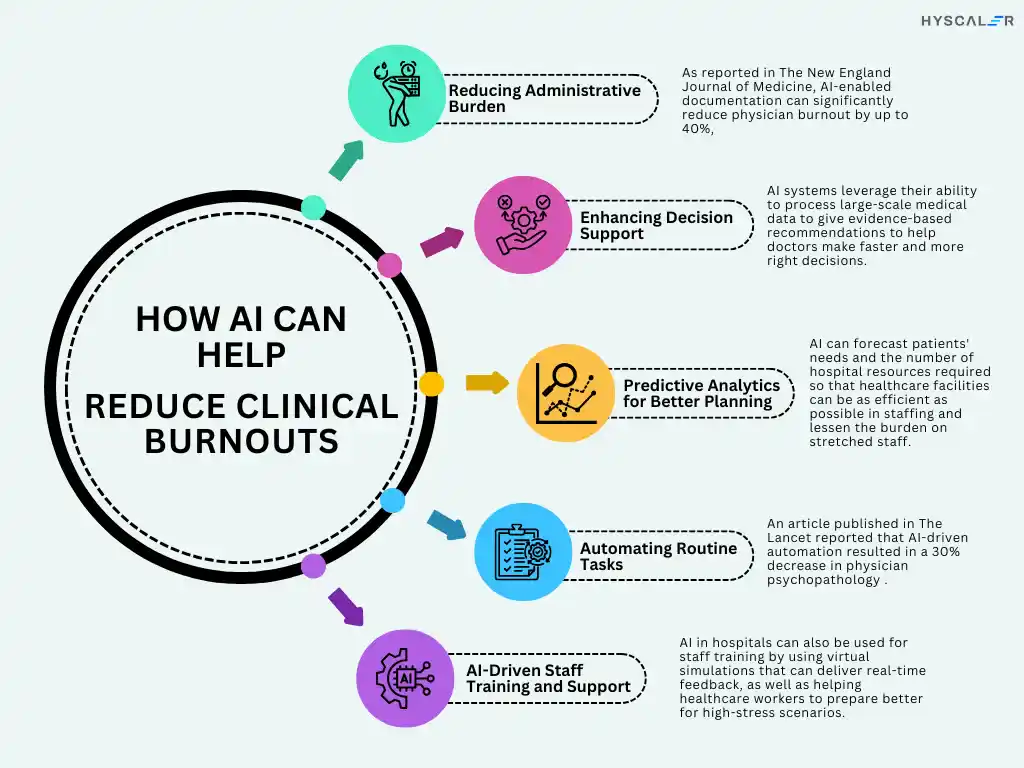
- Reducing Administrative Burden: The workload of medical staff, particularly administrative, is one of the major causes of burnout, i.e. AI-based tools can be used to automate documentation, appointment scheduling, and billing procedures, which then will provide more time for patient care. As reported in The New England Journal of Medicine, AI-enabled documentation can significantly reduce physician burnout by up to 40%, by removing the time otherwise by fostering non-clinical activities.
- Enhancing Decision Support: AI systems leverage their ability to process large-scale medical data to give evidence-based recommendations to help doctors make faster and more right decisions. This support reduces the mental fatigue associated with diagnosis and treatment decisions, improving job satisfaction and reducing stress.
- Predictive Analytics for Better Planning: AI in hospitals can forecast patients’ needs and the number of hospital resources required so that healthcare facilities can be as efficient as possible in staffing and lessen the burden on stretched staff. For example, AI systems can anticipate patient influxes, enabling hospitals to prepare in advance and minimize strain on staff.
- Automating Routine Tasks: Many healthcare workers are subject to burnout because of the need to juggle a flow of tasks. AI can perform repetitive work, like surveillance of vital signs, input of patient data, and even response to trivial patient requests, dramatically lowering the level of mental effort. An article published in The Lancet reported that AI-driven automation resulted in a 30% decrease in physician psychopathology through workflow optimization and a decrease in cognitive load imposed by routine work. This trend not only improves morale but also enhances patient care because providers can provide more direct patient contact time.
- AI-Driven Staff Training and Support: AI in hospitals can also be used for staff training by using virtual simulations that can deliver real-time feedback, as well as helping healthcare workers to prepare better for high-stress scenarios. By reducing errors and boosting confidence, AI helps minimize stress and burnout among healthcare professionals, making them more effective in their roles.
Unveiling the Challenges and Solutions of AI in Hospitals
Despite the excellent promise of AI in hospitals to address burnout and increase efficiency, its implementation is associated with several challenges. Comprehending and dealing with these challenges is essential for guaranteeing the efficacy, ethicality, and positive impact of AI in hospitals. Here are some key challenges and potential solutions:
Resistance to Change
Challenge: The use of AI in hospitals might be deterred by worries related to AI’s effects on human performance, dislikes of new technology, or anxiety related to the replacement of jobs.
Solution: Education and training are essential to easing this resistance. By involving healthcare workers in the AI implementation process, demonstrating the benefits of AI, and emphasizing that AI is a tool designed to support—not replace—human workers, hospitals can foster a more accepting environment. Studies indicate that 70% of AI adoption failures in healthcare are due to resistance from staff, highlighting the importance of strong leadership and continuous professional development.
Data Privacy and Security
Challenge: Hospitals generate large amounts of valuable patient information and to develop serious applications of AI, serious measures of data security are needed to avoid attacks.
Solution: The development of AI tools that comply with stringent data privacy standards, including HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), is highly desirable. AI platforms need to provide high-level encrypted technology, secured ability to access data, and 24-hour-a-day observation to maintain patient data privacy. A study by McKinsey Company found that 70% of healthcare leaders believe improving cybersecurity will be critical to successfully integrating AI in hospitals.
AI Implementation Costs
Challenge: The initial cost of integrating AI technologies can be a significant barrier for many hospitals, especially smaller institutions with limited budgets.
Solution: Hospitals are encouraged to weigh long-term cost and efficiency-saving potential in evaluating the cost of AI implementation. While the initial cost of AI technology is often significant, AI in hospitals can lower operating costs over the years through automation of administrative functions and improvements in the quality of care. As an example, Forbes News indicated that hospitals utilizing AI technologies, as the respondents have reported a 20%‐lower operation cost over the subsequent 1 year of its introduction to the hospitals, due to better resource allocation and error reduction.
Maintaining Human Element in Care
Challenge: Although AI can be used to increase amounts of efficiency, there is one worry that AI’s introduction can diminish the human touch to patient care, a vital factor in achieving a tie of trust and empathy between the provider and the patient.
Solution: AI in hospitals should be seen as a complementary tool rather than a replacement for human interaction. For instance, AI in hospitals can provide support for administrative work or decision-making, freeing healthcare professionals to dedicate more time to their interactions with patients. This guarantees that the human touch will always be at the center of patient care, but take advantage of the effectiveness of AI. Studies published in Harvard Business Review reported that 77% of patients still want a human provider, but also think AI can lead to greater care efficiency.
Ensuring AI Accuracy and Bias Reduction
Challenge: AI systems are only as smart as the data they are trained in. When the training data for AI models is biased or erroneous, it results in inappropriate suggestions and decision-making.
Solution: Hospitals need to ensure that AI models are trained on large, representative, and high-good quality data sets whilst also undertaking regular verifications for accuracy and fairness. Incorporating diverse patient data can help minimize biases. Additionally, continuous monitoring and updating of AI models are essential to maintain their reliability and relevance. A Nature Medicine study found that regularly retrained and fine-tuned AI algorithms demonstrated a 15% improvement in decision accuracy and decreased bias.
Integration with Existing Systems
Challenge: Integrating AI in hospitals can be complex, especially if the hospital uses outdated or incompatible systems.
Solution: AI vendors should work closely with healthcare institutions to ensure seamless integration with existing electronic health record (EHR) systems and other hospital management tools. Hospitals need to invest in scalable, flexible AI solutions that can grow with the requirements. Successful integration has been shown to improve workflow efficiency, and a study by McKinsey found that hospitals that invested in AI-enabled systems saw a 30% increase in operational efficiency after overcoming initial integration hurdles.
To Sum It Up: A Vision for Smarter, Burnout-Free Healthcare
The integration of AI in hospitals is not just a technological advancement—it’s a transformative step towards addressing some of the most pressing challenges in healthcare today, particularly burnout among healthcare providers. By automatizing administrative tasks, and improving decision-making and resource allocation, AI can alleviate the cognitive and emotional burden on medical workers providing a healthier, more productive work environment.
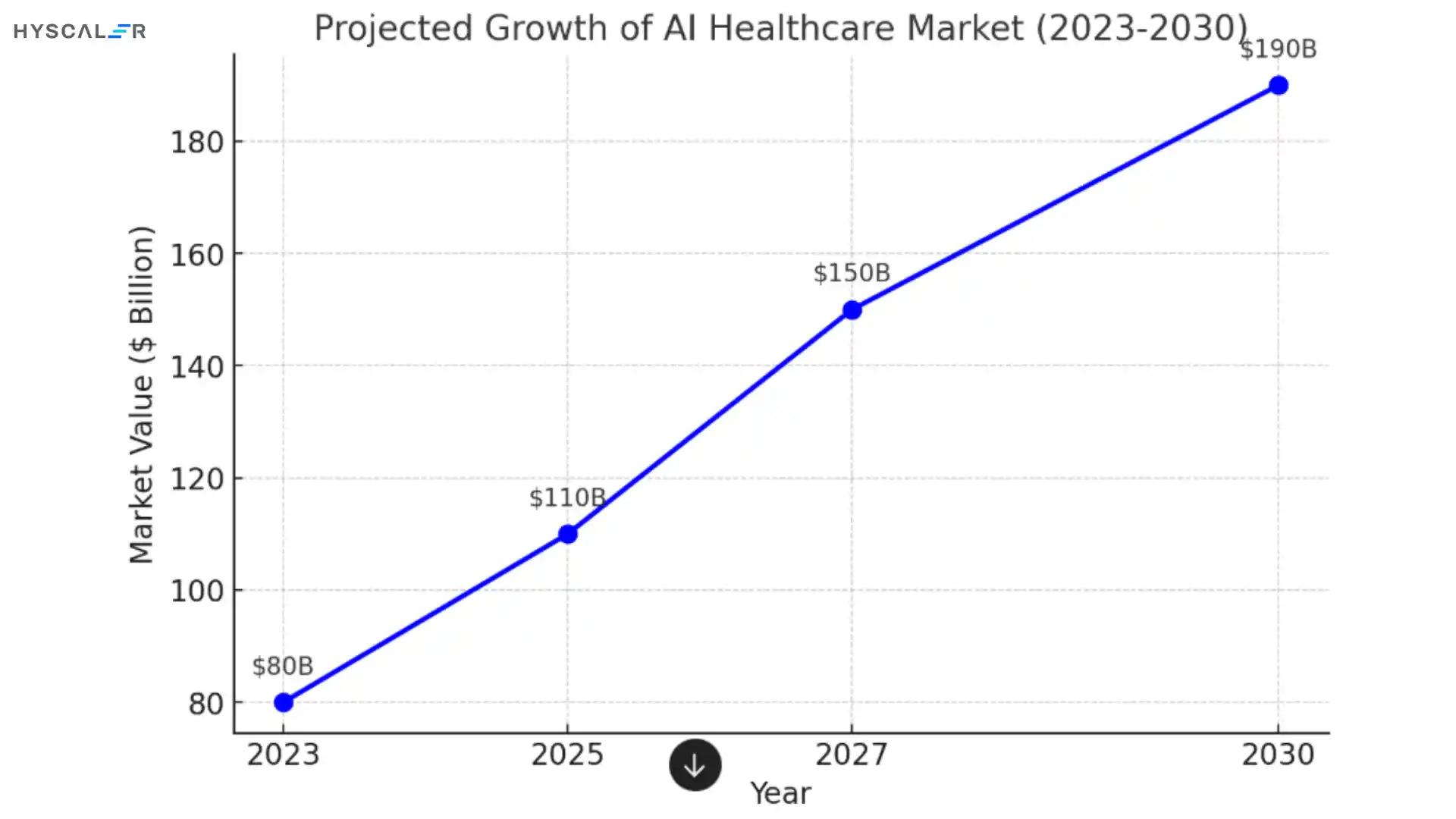
Moving forward, the size of the AI healthcare market is forecast to increase at a yearly compound growth rate (CAGR) of 37% between the years 2023 and 2030, and $190 billion by 2030. This expansion points to the growing importance of artificial intelligence (AI) in changing global healthcare systems, enhancing providers’ sustainability and patients’ health.
Hitting the road to make hospitals rethink burnout and efficiency? Let’s take the first step towards AI solutions today to realize the future of smarter, kinder care.