Table of Contents
Gamification technology in education is revolutionizing some aspects of traditional teaching by introducing game-like mechanics in learning environments. According to a 2021 report published by EdTech Research Group, 70% of students claim that their willingness to learn increases when teachers use gaming elements in the teaching process. Another research article, published in The Journal of Educational Psychology, reported that this percentage decreases the retention rate of educational material and increases the student engagement rate up to 60%.
Education services are critical due to ongoing advances in habits and technology. Among those innovations, gamification—the use of game-design elements in non-gaming contexts—is proving to be an excellent and powerful driver of learning enhancement. Gamification will be changing and transforming education and needs to be prioritized as it engages and invigorates the students. The article deals with gamification and its definition, uses in education technology and science, potential future trends, challenges, benefits, and impact.
What is Gamification?
Gamification is defined as bringing a game perspective, such as points badges, leaderboards, and levels, to our traditional non-game settings with the aim of engagement and motivation. In the case of education, it turns learning tasks into enjoyable and engaging activities. Through such strategy, the competition, the need to succeed, and to work together in teams are directed to achieve active participation and a feeling of accomplishment.
Formally, gamification exploits common human motivation by containing features such as challenges, goal framing, teamwork, rivalry, and progress monitoring. This leads to engaging environments where students actively interact with their work. In contrast to common gaming, the goal of which is quite the domain of amusement, gamification applies these mechanisms in live, everyday life situations to solve problems and meet objectives.
Gamification Technology in Education: Transforming the EdTech Landscape
Gamification technology in education is progressively one of the most important elements of the EdTech landscape, transforming the relationship between educators and students and the way they use learning platforms. The combination of game-based strategies in digital learning spaces not only increases engagement but also increases knowledge. There are numerous EdTech platforms that are using gamification to guarantee that learning is an engaging, immersive, and personalized activity in their learning process.
Following are a few of the most disruptive uses of gamification technology in learning:
Personalized Learning Paths: Platforms such as Duolingo use gamified streaks, levels, and challenges that are adapted to the user’s pace, a powerful motivational mechanism for self-paced learning. Indeed, Duolingo states that 95% of users maintain regular engagement using gamification features when completing lessons.
Interactive STEM Learning: Tools such as Kahoot! And Minecraft: Education Edition integrates problem-solving and exploratory play so that students can practice collaboratively coding and critical-thinking drills. These platforms have been demonstrated to enhance computational thinking and creativity by incorporating problem-based situations from real-life scenarios. As an example, Minecraft Education Edition has been used in countries with more than 100 different countries, and nearly 10 million students are actively learning it through interactive problem-solving.
Skill Development and Assessment: Gamified platforms include quizzes, simulations, and case-based learning tools. These systems provide instant feedback to help students identify and correct gaps in their understanding. Platforms like Quizlet and Classcraft have proven effective by gamifying formative assessments and helping students grasp challenging concepts in real time.
Collaborative Learning: Gamification fosters peer-to-peer learning through leaderboards and team challenges. Leaderboards foster healthy competition and team-based challenges foster teamwork and common problem solving. According to EdTech Journal, peer collaborative learning through gamification improves overall learning results by 45%.
Virtual Simulations for Practical Skills: Simulations are another key application of gamification in EdTech. Students can be exposed to virtual experiments and realistic-world situation simulations (e.g., Labster, SimCity EDU) in which they may be exposed to the opportunity for hypothesis testing, strategy exploration in problem-solving, and hands-on experience. For instance, Labster allows students to conduct technically challenging science experiments within an environment that is risk-free (virtual lab), so as to comprehend high-level scientific abstract notions without having to go through physical labs. As noted by Educause Research, gamified virtual simulations yield increased comprehension by as much as 50%.

First Movers in Action: How Early Adopters are Shaping Gamification Technology in Education
Pioneers in education who employed gamification technology have been fundamental in proving its efficacy, scaling up its deployment, and paving the way for its wider use throughout schools, regional authorities and entire nations. As trailblazing organizations and governments, by using gamification approaches, have been able to teach their students and improve learning results and can help to overcome the accepted educational transgressions.
Montour School District (Pennsylvania): This U.S.-based school district was one of the pioneers to implement games into their education. Using platforms like Kahoot! As well as interactive problem-solving games, Montour could achieve a heightened level of student participation and motivation and also increase the level of understanding rates.
South Korea: South Korea has turned over its education to a technophilic, gameified model and has so done on a national scale. Gamification technologies are employed in STEM classrooms and coding programs to increase creativity and motivation. With its emphasis on game-based learning, it has led to a 25% rise in student engagement rates, as reported by EdTech Insights.
Singapore: Gamification is now embedded in Singapore’s national curriculum, using tools such as Minecraft: Education Edition and related interactive EdTech platforms. Such strategies have proven effective at integrating, within the same learning, real-world problem-solving, creativity, and innovation.
Global EdTech Initiatives: Several, international programs and organizations including UNESCO and EdTech Global point to the experience of successful gamified learning systems in countries experimenting with these applications. These projects demonstrate significant, measureable increases in outcome, with early adopters reporting together a 30% increase in motivation and engagement of varied student demographics.
Game On or Game Over? Navigating the Challenges of Gamification in Education
Gamification technology in education promises exciting possibilities, but like any game, it comes with its own set of hurdles. While integrating game-like elements into learning is innovative, schools and educators must address key challenges to ensure its success. Here are five major challenges that schools are encountering:
Over-Reliance on Rewards: If external rewards, like points, badges, and leaderboards are the main driving factor, students can fall into the trap of prioritizing competition over real learning. There is evidence from research that over reliance on extrinsic incentives can lead to a decrease in intrinsic motivation, propelling students’ learning away from discovery and deep knowledge and towards “getting the trophy.
Digital Divide and Accessibility Issues: Not every student has equal opportunity to access the required devices, internet connection, or technical assistance available on gamified learning platforms. This has lead to a digital divide that puts on the back financially less privileged students and increases the disparity in education. If these disparities are not addressed, gamification is susceptible to leaving out certain segments of the learners.
Complex and Expensive Implementation: A successful gamified learning experience demands careful design, resources, and expertise. Schools are continuously challenged by technology, time, and training costs. However, gamification without the corresponding investment and preparation may be a poor tool or a tool that is out of sync with real learning goals.
Risk of Gaming Addiction and Distraction: Although gamification is supposed to be entertaining and fun to learn, it can result in some undesirable behavior, that is, the excessive play time, or preoccupation with points, and neglect to learning results. Such phenomenon can negatively impact academic performance and potentially students will focus more on the rewards than on learning process. To mitigate these risks engagement must be maintained in balance with purpose.
Teacher Preparedness and Training Needs: With gamification, teachers are key to delivering effectiveness, however, the training or confidence to incorporate these tools into classes is not seen by many educators. Unaided by adequate support, professional development, and recognition of the alignment between gamified platforms and curriculum goals, teachers may lack the means to guarantee that gamification has an effect that is meaningful to learning.
Leveling Up the Classroom: Exploring Future Trends in Gamification in Education
Gamification in education is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and innovative teaching approaches. As educators and technologists look to the future, several exciting trends are shaping how gamification will redefine learning experiences for students. Here are the key trends expected to transform the role of gamification in education:
- AI-Powered Personalized Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is poised to transform the use of gamification in educational platforms. AI will enable dynamic real-time personalization of students’ learning trajectories by scaling challenges based on their individual strengths and weaknesses and on their performance. Using AI, learning will be hyper-personalized such that every student is given the appropriate level of challenge at the appropriate time to stay challenged and succeed.
- Integration of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR, and VR, will help put immersive learning experiences at the heart of gamification. These technologies have the capacity to change the conventional class into hands-on experiences, from visiting the past through AR, carrying out virtual science and measurements, or rehearsing reality in a safe simulated context. These tools can turn abstract ideas into concrete items, thus leading to better comprehension and participation of students.
- Blockchain for Secure Credentialing and Rewards
Blockchain technology will be more and more used to guarantee security, transparency and verifiability of accomplishments in gamified learning environments. This approach could have a game-changing effect on how students acquire micro-credentials, badges, and other forms of recognition by establishing verifiable, recordable, and blockchain-secure certificates of learning which may be transferred, for example, between institutions or directly to a professional job application.
- Expanding the Scope to Social-Emotional Learning (SEL)
Gamification will also grow out of the domain of academic skills to social-emotional skills. Students will gain experience in working together, in conflict resolution, in developing empathy, and in managing emotions through game-based simulation and cooperative tasks. This methodology encompasses emotional intelligence in the way they learn, which consequently prepares them for real-life interpersonal challenges.
- Cross-Platform Learning Integration
The next era promises gamification design integrated in any digital learning space including mobile apps, virtual classrooms, and other interactive online tools. The cross-platform accessibility allows that gamified learning may be uniform, personalized, and available regardless of the device or media used by students, i.e., a cohesive and immersive learning space.
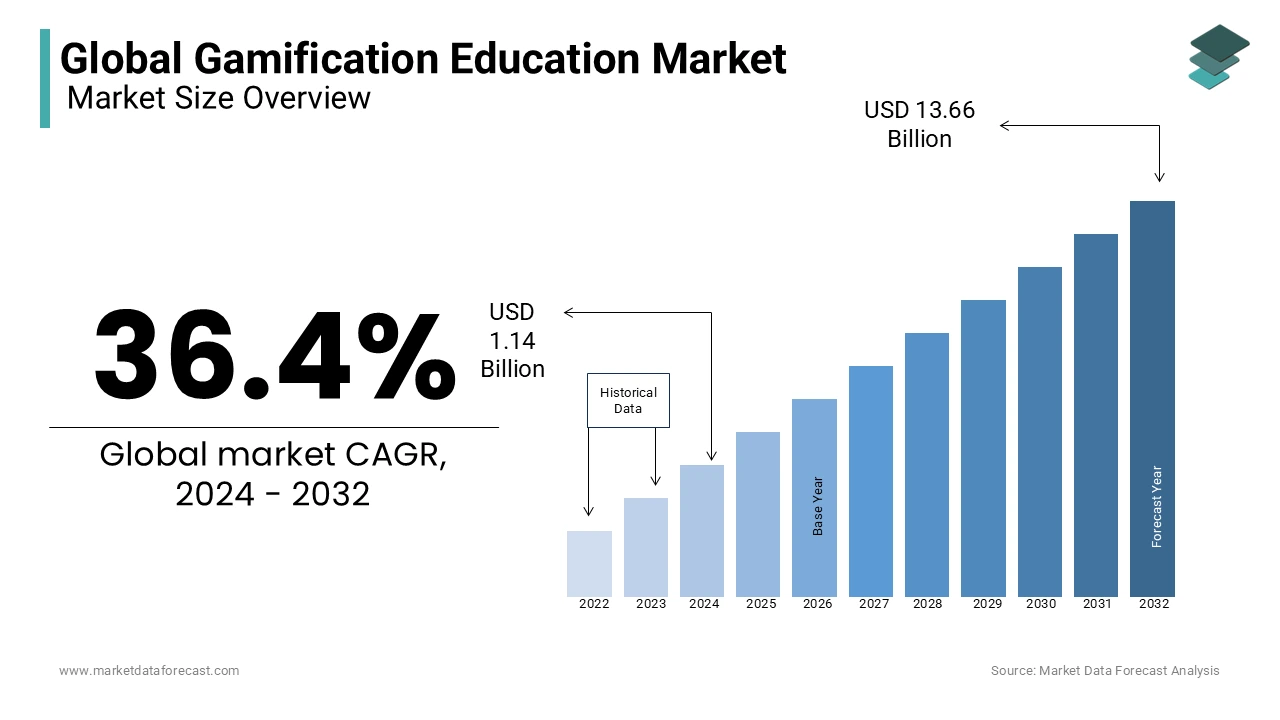
Closing the Chapter: The Transformative Power of Gamification in Education
Gamification technology applied to education has been shown to be more than just another fad, but a paradigm shift, which can rewrite the relationship between students and teachers and learning itself. As reported by ISTE, gamification not only can raised student’s engagement by 60% and academic retention rates by 20%, it must also be noted that introducing game-like mechanics into learning environments offers concrete benefits.
From platforms like Duolingo encouraging consistent self-paced language learning to Minecraft: Education Edition sparking creativity through problem-solving, these tools demonstrate how interactive strategies can make learning both enjoyable and impactful. While challenges such as technological accessibility, design complexity, and dependency on extrinsic rewards exist, they can be addressed through thoughtful implementation and innovative thinking.
The journey of gamification technology in education is far from over. The evidence is compelling, the opportunities are endless, and the call is clear: educators, innovators, and policymakers must embrace this approach to unlock the full potential of every learner. Let’s step into this exciting future and transform the learning experience for all.