Table of Contents
Nanorobotics represents a cutting-edge field at the intersection of nanotechnology and medical science, offering unprecedented potential in minimally invasive surgery. In this article, we delve into the remarkable world of nanorobotics and its pivotal role in reshaping the landscape of medical procedures.
The significance of nanorobotics lies in its ability to revolutionize the way surgeries are performed, fundamentally altering the healthcare landscape. Traditionally, surgical procedures have often necessitated large incisions, resulting in prolonged recovery times, heightened pain, and an increased risk of complications. However, with the advent of nanorobotics, a new era has dawned in the field of surgery.
1. The Rise of Minimally Invasive Surgery
Traditional surgical procedures typically involve large incisions made by surgeons to access and treat internal organs or tissues. These procedures often require patients to stay in the hospital for an extended period and involve longer recovery times.
- Large Incisions: Conventional surgeries necessitate significant incisions, which can result in more significant scarring and an increased risk of infection. Patients may experience pain and discomfort at the incision site.
- Extended Hospital Stays: Patients undergoing traditional surgery usually need to stay in the hospital for several days or even weeks, depending on the complexity of the procedure. This can lead to higher healthcare costs and a greater risk of hospital-acquired infections.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Surgery
Minimally invasive surgery, on the other hand, represents a revolutionary shift in the field of surgery. It offers numerous advantages, including:
- Smaller Incisions: Minimally invasive procedures involve tiny incisions, often just a few millimeters in size. These small openings are less painful, heal faster, and leave minimal scarring compared to traditional surgical incisions.
- Reduced Pain: Minimally invasive techniques are associated with less postoperative pain. Patients typically require fewer pain medications and experience a quicker return to their normal activities.
- Faster Recovery: The recovery time for minimally invasive surgery is significantly shorter than that of traditional surgery. Patients can often go home the same day or within a shorter hospital stay, leading to reduced healthcare costs and a faster return to their daily lives.
Growing Demand for Less Invasive Techniques
- The demand for minimally invasive surgical techniques has been steadily increasing over the years. Patients are becoming more informed about their healthcare options and actively seeking procedures offering less pain, shorter recovery times, and fewer complications.
- Surgeons and medical professionals also recognize the benefits of minimally invasive approaches, which have become standard practice for various medical specialties, including cardiology, gastroenterology, and gynecology.
2. What Are Nanorobots?
Nanorobots, also known as nanobots or nanomachines, are tiny robotic devices with dimensions on the nanometer scale, typically ranging from one to a few hundred nanometers. These minuscule machines are designed to perform precise tasks at the molecular or cellular level within the human body and other environments.
Characteristics of Nanorobots
- Nanorobots are characterized by their small size, remarkable precision, and ability to operate in confined spaces. These devices are often built using advanced nanoscale materials, such as carbon nanotubes or DNA origami, which allow for both structural stability and flexibility.
- Additionally, nanorobots are engineered to carry out specific functions, such as drug delivery, tissue repair, or diagnostic tasks, depending on their intended applications.
Design and Control of Nanorobots
- The design and control of nanorobots are complex processes that require interdisciplinary expertise in fields like nanotechnology, robotics, and biomedical engineering.
- Nanorobot design involves selecting suitable materials and components, such as sensors, actuators, and propulsion systems, to achieve the desired functionality.
Nanoscale Dimensions
- One of the defining features of nanorobots is their nanoscale dimensions. To put this in perspective, a nanometer is one billionth of a meter, or roughly 100,000 times smaller than the diameter of a human hair. This tiny scale grants nanorobots access to regions of the body that were previously inaccessible using traditional medical tools.
- Their small size enables them to navigate through blood vessels, target specific cells or tissues, and perform precise interventions with minimal disruption to surrounding structures.
Nanorobots are cutting-edge devices designed to operate at the nanoscale, performing intricate tasks in various fields, including medicine. Their small size, carefully crafted design, and innovative control mechanisms make them promising tools for revolutionizing healthcare and a wide range of other applications.
3. Nanorobots in Medical Applications
Nanorobots have shown immense promise in a wide range of medical applications, with their ability to operate at the nanoscale offering unique advantages.
- Drug Delivery: Nanorobots have the potential to revolutionize drug delivery in medicine. These tiny machines can be designed to carry and release drugs with precision, ensuring that medication reaches its intended target in the body. For instance, nanorobots can be programmed to navigate through the bloodstream, deliver drugs to specific cancer cells, and release the medication precisely where it is needed.
- Targeted Therapy: Nanorobots enable targeted therapy by selectively delivering treatments to diseased tissues or cells while sparing healthy ones. For example, in cancer treatment, nanorobots can be equipped with sensors that detect cancer markers. Once detected, they can deliver therapeutic agents directly to cancer cells, increasing the specificity of treatment and reducing damage to surrounding tissue.
- For instance, researchers are exploring the use of nanorobots to deliver insulin to diabetic patients, monitor glucose levels, and provide on-demand insulin release. Additionally, in neurology, nanorobots are being investigated for their potential to navigate intricate neural pathways and deliver therapeutic agents to treat neurological disorders.
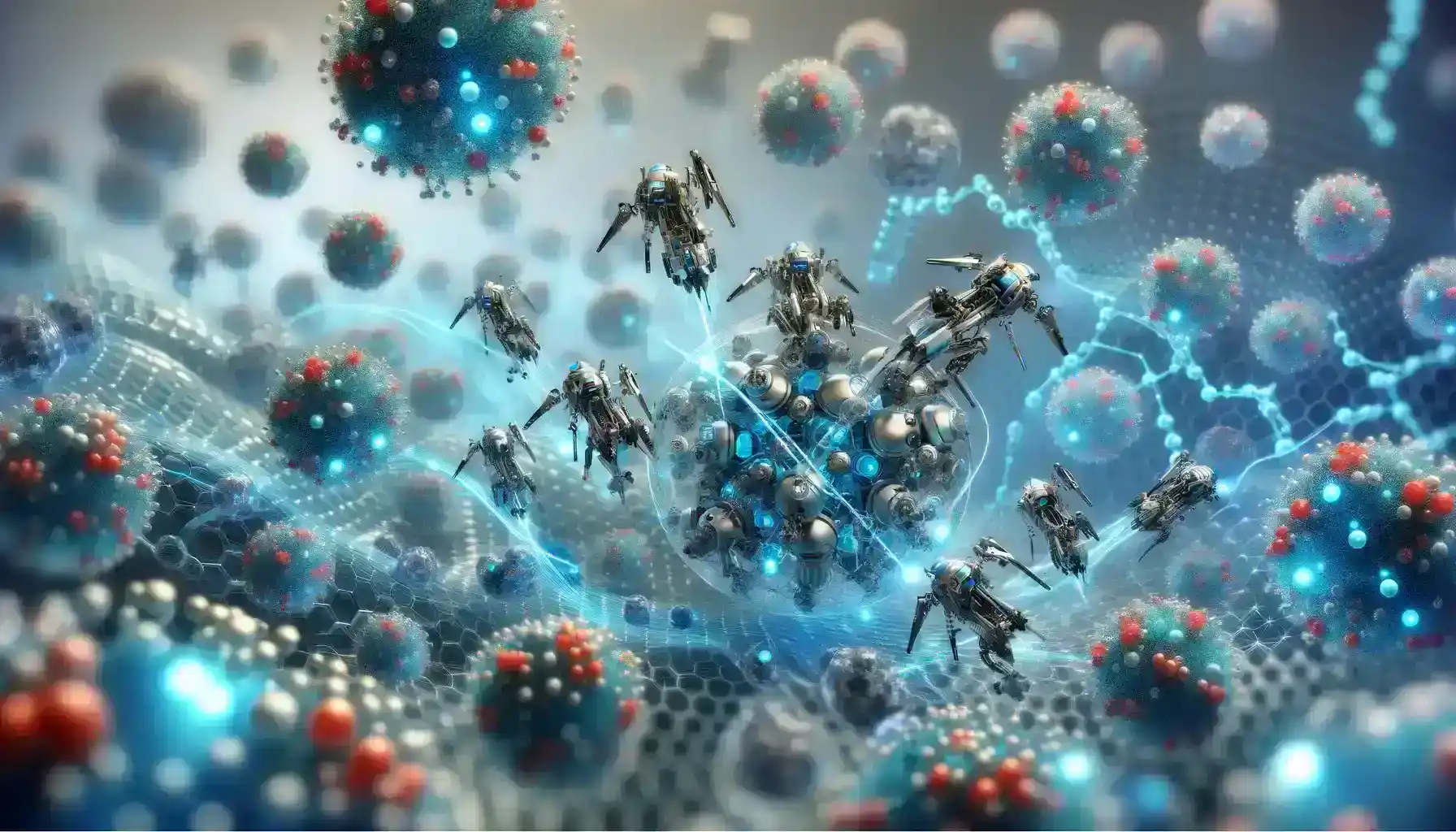
4. The Role of Nanorobotics in Minimally Invasive Surgery
- Nanorobotics has emerged as a groundbreaking technology with the potential to revolutionize minimally invasive surgery, offering a multitude of advantages that can significantly enhance the precision and outcomes of surgical procedures.
- Nanorobotics, which are minuscule robotic devices at the nanoscale, hold the promise of transforming the landscape of surgery. Their tiny size allows them to navigate through the human body with unprecedented precision, accessing remote or delicate areas that were previously challenging to reach through conventional surgical means.
- Blood Vessel Maintenance: Nanorobots can patrol the circulatory system, detecting and repairing damaged blood vessels. In cases of arterial blockages, nanorobots equipped with tools for removing plaque can restore blood flow without the need for invasive surgery, reducing the risk of strokes and heart attacks.
5. Challenges and Ethical Considerations
- Nanorobotics in surgery presents several challenges and limitations that need to be carefully considered. Firstly, ensuring the safety of nanorobots within the human body is a significant concern.
- As these tiny devices navigate through intricate biological systems, there is a risk of unintended side effects, such as tissue damage or triggering immune responses.
- Engineers and researchers must develop robust safety protocols to mitigate these risks. Moreover, the complexity of nanorobotic systems can pose technical challenges.
Ethical Considerations in Healthcare
- The integration of nanorobotics into healthcare raises important ethical considerations. One key concern is patient consent and privacy. Patients must have a clear understanding of the use of nanorobots in their treatment and provide informed consent.
- Additionally, the data collected by these devices, such as real-time health information, must be managed ethically and securely to protect patient privacy.
- Ethical consideration is equitable access to nanorobotic healthcare. As this technology advances, it’s crucial to ensure that it benefits a wide range of individuals and does not exacerbate healthcare disparities.
- Nanorobotics in surgery holds great promise, but it also presents challenges related to safety, technical complexity, and ethical considerations. Ongoing research and collaboration are key to overcoming these challenges and realizing the full potential of nanorobotics in improving healthcare.
6. The Future of Minimally Invasive Surgery
The future of minimally invasive surgery is undeniably intertwined with the exciting advancements in nanorobotics. As technology continues to evolve, so does the potential for nanorobots to redefine surgical procedures in profound ways.
Emerging trends also point to the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into nanorobotic systems. AI-driven algorithms will enhance the decision-making capabilities of nanorobots, allowing them to adapt to dynamic surgical environments and respond to unexpected challenges. This fusion of nanotechnology and AI promises to reduce the margin of error in surgeries and improve patient outcomes.
First and foremost, we foresee increasingly sophisticated nanorobots that are capable of performing intricate surgical tasks with unparalleled precision.
The transformative potential of nanorobotics in minimally invasive surgery cannot be overstated. The synergy between nanotechnology and surgery is poised to reshape the healthcare landscape in the coming years.
As we look to the future, the prospects are bright. We anticipate nanorobots becoming indispensable tools in the hands of skilled surgeons, enabling procedures that were once thought impossible.
The future of healthcare is being shaped by these tiny yet powerful agents, and staying abreast of these advancements will not only benefit patients but also contribute to the growth and improvement of the healthcare industry as a whole.
Embrace the future with us, where nanorobotics pave the way for safer, more precise, and minimally invasive surgeries, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for countless individuals.